This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful. More information.
SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION
A. INFORMATION
B. INTERNAL SEO
C. EXTERNAL SEO
D. TECHNICAL SEO
Honest information about search engine optimization
Search Engine Optimization (also known as SEO or Organic Search Optimization) is the art of raising a website’s ranking in the organic search results of Google and other search engines.
Search engine optimization helps customers find the right product or service at the right time – and with the right keywords (search terms).
Successful search engine optimization is often the best marketing investment for a company that conducts business online – and the results achieved are long lasting.
Read more about the benefits of SEO.
Free SEO tools
We included two very useful SEO tools in this guide:
SEO TEST – Test your website’s current SEO status. Get your free test results right away!
SERP TEST – Create page titles and meta descriptions according to Google guidelines. See what your page will look like in Google’s organic search results.
We do customer-focused search engine optimization
This means that, in addition to the search engines, we take your customers into account when designing our strategy. It ensures that the results are good for human visitors as well as the search engines, giving you more revenue-generating traffic and more satisfied customers.
This SEO guide honestly explains how search engine optimization really works. We’ve skipped all the unnecessary clichés and instead focus on how it’s actually done – even if Google or other guides argue otherwise.
After reading this guide, you will know all the important steps in search engine optimization and gain good insight into how to optimize your web pages.
You can find more information in our SEO blog, and if you need professional help, we also offer SEO services.
Before we begin, we will go over a few points about the profitability of search engine optimization and the main reasons for optimizing your website. You can already begin to internalize the idea that “Successful SEO is a jackpot for any company.”

Google is the most important search engine
Internet users prefer the Google search engine by far. About 97% of searches on computers and 99.5% of searches on mobile are done through Google.
For this reason, the purpose of search engine optimization is primarily to increase the ranking in Google’s search results.
In addition, Bing, Yahoo and other search engines will appreciate the same actions as Google does, so visibility is usually improved in all search engines – even if you focus entirely on Google.
The first couple of search results get almost all the traffic.
Organic Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
Here you can see the average clickthrough rate for each position in Google's search results. The values in the table are based on statistics for more than 4 million keywords on 36,000 web pages.| Position | Mobile | PC |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 29,70% | 37,65% |
| 2 | 16,91% | 18,15% |
| 3 | 10,73% | 10,89% |
| 4 | 7,22% | 7,26% |
| 5 | 5,13% | 5,22% |
| 6 | 3,74% | 3,89% |
| 7 | 2,76% | 3,01% |
| 8 | 2,08% | 2,40% |
| 9 | 1,57% | 1,95% |
| 10 | 1,18% | 1,70% |
| 11 | 1,13% | 1,84% |
SEO Guide
Our SEO guide is made in a more honest way than most other search engine optimization guidelines.
Instead of just repeating Google’s guidelines, we tell you what actually works.
Our goal is for every website owner to understand the importance of search engine optimization, because any company with business online simply can’t do well without good organic search results.
Audit and SEO test your website now!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
This guide is long, but you can use the links below to jump to the right section.
A1. What is Search Engine Optimization?
A2. How does SEO pay off?
C1. Trust
C2. Link research
C3. Link building
C4. Anchor texts
B1. Nyckelordsforskning
B2. Keyword plan
B3. Page titles
B4. Meta descriptions
B5. SERP Test
B6. Content
B7. Internal links
D1. Page load speed
D2. Responsiveness
D3. Navigation and menus
D4. Page URL address
D5. Redirection and HTML-tags
D6. Negative SEO
D7. Analysis and SEO tools
A. INFORMATION
A1. What is Search Engine Optimization?
Search engine optimization, also known under the abbreviation “SEO”, is a way to improve a website for both search engines and its users.
The purpose of search engine optimization is to make web pages rank higher in the search results when a user searches for a relevant keyword. The optimized page is thus easier to find, and the visitors are already looking for the products or services you offer.
The optimization is about improving everything from the technical and structural aspects of the page, to its design and the content itself.
Distribution of searches in the most popular search engines:
- Google 98.08%
- Bing 1.48%
- Yahoo 0.25%
- Ask 0.06%
- Yandex 0.05%
Actually, the second most popular search engine is the video platform YouTube, which is also owned by Google, but in this guide we focus on information search. However, the same principles generally apply to ranking videos as well.
A2. How does SEO pay off?
A well search-engine-optimized site generates free traffic from Google searches. When the project is carried out correctly and without risky measures, the foundation is laid for continually rising trends.
The more keywords your site appears for in Google search results, the more potential customers will find your business.
Since the traffic generated from search engine optimization is basically free, it is usually the most cost-effective way to reach customers in the long term.
“Without good search engine visibility, the outlook for any online business is not very good.”
To make it easier to understand the financial benefits of SEO, we have compared the cost of search engine optimization with paid advertising through Google Ads.
NOTE! This example explains theoretical costs, based on imaginary traffic and clicks. In practice, the best results are achieved by ensuring good visibility in both paid and organic search results.
In this example, the cost of search engine optimization is 46 000 € / 3 years.
The theoretical total cost of paid advertising is 375 908 € / 3 years.
Furthermore, thanks to the search engine optimization, the amount of organic traffic would remain at the same level after the three years with only maintenance costs, at a price of 0.039 € per visitor (750 € / month).
The cost of Google Ads advertising remains at 0.8 € per visitor (14 080 € per month)
Read more about our services

B. INTERNAL SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION
B1. Keyword Research
Keyword research is about finding the best keywords for each individual page.
It’s usually not possible to guess at all the keywords and varations, so it’s worth using SEO tools to get additional information.
Although search volume is an important factor, keywords should not be chosen solely by volume.
Relevance is more important than search volume.
The targeted keywords must describe the content of the page well. It doesn’t matter if a particular word doesn’t have a large search volume, as long as it fits into the page. There is often lower competition for keywords that do not have the highest search volume, so a higher position can be reached with less effort.
During your keyword research, you will also learn to find lots of words and phrases that have many searches but do not fit the page you are creating. You should note these search terms somewhere, as you can later create additional pages or blog posts that target them.
Example: You have a store that mainly sell sunglasses. Your keyword research leads to many search terms based on the broader word “glasses”. You cannot use the word on the sunglasses page, because the keyword does not match the content of the page.
Select only the most relevant keywords
It is a good idea to spend enough time on keyword research, as it will affect the future traffic to your site.
The more relevant the keywords, the greater the proportion of visitors will be converted to customers.
Be mindful when choosing keywords: If you choose the word “shirts” for a page of women’s clothing, the conversion rate might not be very good, because even those looking for men’s or children’s shirts may accidentally end up on this page.
At the same time, you can take advantage of keyword variations if you distribute the pages correctly. If the keyword “men’s shirts” leads to a page with men’s shirts, while “women’s shirts” lead to the page of women’s shirts and “shirts” to a page with all shirts, etc. Thus, the different keywords and the different pages do not compete with each other, and maximizes the search visibility of your site with all these keywords.
Keep the difficulty of the keyword in mind. Trust is lower for a new website than an established site, at least in the eyes of the search engines. If you compete with the same keywords as old and trusted websites, it is difficult to see results quickly.
A good example is a clothing store such as Zalando, which dominates the clothing market online. If you sell the same products and compete with the same keywords, you probably won’t rank higher than them.
To think about when choosing keywords
- The keyword must fit the page perfectly = the more relevant, the better the conversion rate
- The keyword must have search volume = the higher the volume, the more potential visitors
- Keyword competition = how many other websites are trying to rank for the term?
Recommended Keyword Research Tools:
- SEMrush – Paid service
- KWFinder – Paid service
- Keywordtool.io – Paid and free version
- Google Ads Keyword Planner – Free service from Google
- Ahrefs – Paid service
Need help with keyword research?
B2. Keyword Plan
Now that you know how to do keyword research, you can take another step forward and create a keyword plan.
The keyword plan specifies how to use the selected keywords on the site.
The easiest way to create a plan is to list all the pages that should be optimized in a spreadsheet and then select the best, most relevant keywords for each page.
It is not recommended to choose too many keywords per page. Select the main keyword and a few relevant search terms that can be used in your content.
When choosing keywords, keep the following criteria in mind:
- Relevance
- Search Volume
- Competition
- Your own judgement
NOTE: Avoid using the same keywords on multiple pages. Use internal links to indicate which page should rank for common terms.
The more keywords and keyword groups you divide into different pages of your site, the more relevant traffic you will get to your site (provided your keywords are ranking well within Google search results).
A broad or narrow search plan?
As mentioned, it is not advisable to select keywords solely for search volume. You should always think about how well the terms fit the intended page. If there is a large product range or a large amount of pages, there will be more suitable keywords.
- The main keywords have 32,300 monthly searches
- The average difficulty level is 30/100
- The average search volume is 10,766
| Keyword | Difficulty | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Honor 7 lite case | 15 | 90 |
| Honor 7 case | 9 | 110 |
| Huawei p8 lite case | 13 | 210 |
| iPhone 6s case | 8 | 2400 |
| iPhone 7 mobile case | 23 | 210 |
| iPhone 7 case | 17 | 6600 |
| iPhone 8 case | 23 | 6600 |
| Samsung Galaxy S7 edge case | 19 | 720 |
| Samsung case | 21 | 480 |
- The keywords have a monthly search volume of 17,420
- The average level of difficulty is 17/100
- The average search volume per word is 1935
Conclusion
By using a wider search plan, we get higher search volumes with more specialized pages. This is almost always an easier, more sensible option.
This example used only nine keywords. How big would the difference be with hundreds or thousands of keywords?
Although more work is required initially, you will reach far more customers than you would with just a few, broader keywords.

B3. Page Title
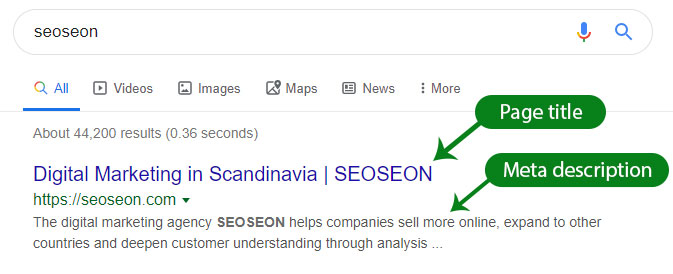
The page title appears in Google search results.
The page title plays an important role in search engine optimization, as they help both search engines and your customers understand what a particular page is about. If the title does not contain the main keyword, the page is unlikely to appear in the search results.
In this section, we will show you how to use page titles to optimize the site. Whether it is an online store, a company website or a personal blog; page title optimization works in the same way.
Before selecting the page titles, the keyword plan must be completed. It helps you see which keyword to use on each page, so make sure the search plan is made for the entire site before you begin.
Each individual page on the site should have its own, unique page title. The content of the page should also be tailored to the keyword. It’s important that Google find just one page for each keyword on your site, so your pages don’t compete with each other.
Length of the page title
Google has chosen to limit the width of the page titles that appear in the search results, which is specified in pixels.
The maximum length of a page title is currently 580 pixels (since December 2017).
It does not mean that you have to fill it completely. Instead, try to create the most descriptive and attractive title.
We have created a SERP preview tool to help you write fitting titles and meta descriptions.
General recommendations for page titles
- Briefly describe the content of the page
- Use keywords (without repeating them)
- Enter the name of your site (eg “Page Title | Example.com”)
- Try to attract clicks
Google’s algorithms evaluate, among other things, the title’s relevance to the search/page, its clickthrough rate and its bounce rate, to determine where your page should be placed in the search results.
A perfect title contains the most important keywords selected for that page.
The main target keyword should always be included in the page title, and preferably at the beginning of it. If a page is targeting multiple keywords, the most important one(s) should be included in the title of up to 580 pixels – and preferably in a readable sentence.
Full Title: Keyword 1 – Keyword 2 | Example.com
Example:
The company Webfirm.xe develops cheap websites for companies and has chosen “website for business”, as well as “cheap websites” as their primary search phrases.
A suitable title might be “Business Website – Cheap Websites | Webfirm.xe”
However, you can use all keywords in a more natural way and create a better title for the site: “Cheap Business Websites | Webfirm.xe”.
It is a shorter, more descriptive and more readable title, which also adds another search phrase: “cheap business websites”.
Enter the page title
In most website builders, the title is automatically taken from the page name. If you want to manually enter the page title in the source code, it must be entered in the HEAD section as follows:
<head>
<title>Enter your page title here | Your.site</title>
</head>

B4. Meta descriptions
A meta description is a brief description of a web page’s content, which can be displayed under the page titles of search results.
Why is the meta description important?
A meta description can affect the clickthrough rate, and thus, the number of visitors to a web page.
If the description of the page is interesting and calls for action, you are likely to get more clicks to your site. In addition, it may contain the keywords, which are bolded in the search results and make your page stand out in the crowd.
Your meta descriptions should be honest and clear, so as not to negatively impact the conversion rate. At the same time, you should try to convey details about the page, and reasons why the customer should choose your website over other search results.
Length of meta description
The maximum length for a meta description is about 155-160 characters.
A longer description or snippet may sometimes be display in desktop searches, but since Google has made its mobile index the primary index, it is recommended to have descriptions up to 158 characters at most.
Include the keywords early in the meta description to ensure they are visible even if the description is cut short.
We have created a SERP preview tool to help you write fitting titles and meta descriptions.
Google can automatically create a description based on your body text, which can be displayed if it is considered more relevant to the search phrase. However, it is still recommended to write a unique description containing the main keyword for each of the pages on your site.
How to add the meta description
Many website builders have a field to enter the meta description, but if not, you have to manually add it to the page’s code.
Example
<head>
<meta name="description" content="The digital marketing agency SEOSEON helps companies sell more online, expand to other countries and deepen customer understanding through data. See our services here!"/>
</head>
Want help with meta descriptions?
B5. SERP Test
A free SEO tool that helps you create page titles and meta descriptions of the right length.
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Page. Here, you can test if your page titles and meta descriptions are of appropriate length. Preview how your page will look in Google’s organic search results, both on PC and on mobile.
Page title goes here…
https://www.example.com/
Your page title is displayed here…
URL address:
Page title: ? / 580 px
Meta description: ? / 160 characters

B6. Content
Body texts and other content is one of the most important criteria for a search engine when organizing search results in ranking. This guide will help you create search engine optimized content.
A common content optimization question revolves around the “keyword frequency”, that is, how many times a particular keyword is mentioned in the content. Once upon a time, it was possible to improve your rankings by simply squeezing in as many keywords as possible.
However, the search engines have become much smarter since then and now you should focus on quality content. Write the content for the users, not for the search engines. Try to answer all questions around the topic and use all relevant keywords (and their variations) naturally throughout the text, without spamming them.
Google is better at English
Although Google has become very good at understanding most languages, the search engine’s understanding of English is still superior. This means that localized optimization may not always be carried out in exactly the same way.
For example, Google understands all synonyms, inflections and variants of words in English, but not necessarily in Swedish or Finnish. That means you should use the exact phrases at least once to make sure Google understands the content.
It is still recommended to use variations and synonyms as well, as long as the content is written in a natural way.
How often should keywords be used in the texts?
If you use the keywords too much and in an unnatural way, the page can be seen as over-optimized. Therefore, only use the keywords in logical, natural places in the text. If you make it clear to a human what the page is about, Google will understand as well.
There are no exact rules for how much content is needed, what is too little or what is too much. In general, you will need more and better content than your competitors, if they have a more trusted site.
If you are worried that you have used certain keywords too much, or not enough, then you can compare with other pages that rank for the same keywords.
Tip: Use the browser extension SEOquake to quickly evaluate competitors’ content.
How many words should I write?
It’s impossible to give an exact answer, because it depends on the topic, focus, competition and other content of the page. For example, product and category descriptions are usually between 200-600 words.
A good example is the web giant Zalando, which uses a short description of about 50 words at the top, above the products, plus a longer description of at least 300 words at the bottom – even in small categories. They contain all the most important keywords, with variations and so-called “long tails”, some of which link to sub-categories.
Long tails are search phrases that include the main keyword along with other words
A blog post should be at least a few hundred words, but the statistics show that longer, more in-depth blog posts tend to rank better than short ones in search results. Try to write the best content and answer all the questions around the topic – instead of merely focusing on the number of words.
The most important thing is that the content on each page is unique!
It is not possible to copy product descriptions from the manufacturer’s website and expect good rankings in the search results. You also can’t use the same generic description for all similar products if you want them all to appear in Google.
Google devalues duplicate content, so don’t underestimate the power of unique content in search engine optimization!
When creating content, keep the following in mind:
- The content must always be unique
- The texts should be written for the visitors, but also contain the keywords
- Include lots of keyword synonyms, variations and long tails
- Longer texts often (but not always) rank better
- Do not exaggerate the use of keywords
Need help with writing excellent, optimized content?
B7. Internal links
Website navigation is an important factor in search engine optimization. At best, internal links are shortcuts to relevant pages, which makes the linked pages stronger in the eyes of the search engines. Link to useful information in your body texts when appropriate and logical.
Links on the home page
From the front page, you’ll want to link to all your most important sub-pages. The home page is almost always the most trusted page on your site – and the pages linked from it are also considered important.
Anchor texts in internal links
In your internal links, you can use the exact keyword that the page you are linking to, but only when it fits naturally into the content.
If you have several internal links to a particular page, you should vary the anchor texts, but keep them very relevant. This helps inform the search engines what the page is about – and which keywords it should rank for.
Internal links are easy to optimize in retrospect. You can use tools like Google Analytics to see how users navigate from page to page and figure out how to facilitate the flow by placing internal links.
Other tools allow you to see all links pointing to a particular page, as well as their anchor texts, so you can see which pages have the most/least number of links, which need more variation in the anchor texts, and so on.
Need help with your internal links?
C. EXTERNAL SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION
C1. Trust
External search engine optimization (“off-page optimization”) is largely about improving the trust and authority of a website. Google uses a variety of factors to evaluate the trustworthiness of a particular site, but links from other trustworthy sites is one of the most important factors. In short:
“Trustworthy websites usually have links from other trustworthy sites.”
Not all links are equal. For a link to be considered as good as possible, it must come from a trustworthy website, from a page with relevant content, and preferably be in the same language as the landing page.
The best tools for measuring trust
There is no exact measurement for “trust”, at least not as defined by Google, but there are several different tools that do their best to measure website trust and authority. The most common, most popular SEO tools are Ahrefs, Majestic, SEMRush and Moz.
They use different algorithms to evaluate websites and they all display their results on a scale of 0-100, where 100 is best. The main factors are the trust of the linking pages, the number of domains that link to the page, and the total number of links. The service Domainstats.com can give you a free summary and overview, without having to pay for SEO tools.
External SEO is very time consuming. Are you running out of time?
C2. Link Research
Link research is about investigating links to your competitors and mapping opportunities for link building.
Link research in five steps:
- Find competitors using keywords from the plan
- Examine their links with SEO tools
- List opportunities + contact information
- Contact the site to discuss linking opportunities
- Approve the links
1. Find your competitors using the keywords from your keyword plan
Find all the websites that rank on the first page for your keywords. In very competitive industries, it may be worth going deeper than the first page. Create a list of competitor websites, broken down by keyword.
2. Use SEO tools to see their links
Export a list of a competitors links to a spreadsheet or CSV file for easier manipulation of the data. Repeat this for all competitors, merge the lists, remove duplicates and sort by the domain trust level. You may also want to remove irrelevant / foreign web sites at the same time.
3. Review the links manually and collect contact information
You can now visit each link manually and note what type of page it is, as well as their contact information. If the page does not seem appropriate to link from, you should strike it from the list.
4. Contact the site administrator
Send an email or call the webmaster, author or editor of the site and ask them if you can get a link, and how. Sometimes you may be able to write a guest post to the page/blog, sometimes you may be added to a list of resellers, and sometimes you may have to pay for the link.
5. Approve the link
You want a relevant link from a strong page on their domain, so negotiate the best opportunity you can. A link that is irrelevant or comes from an untrustworthy domain is not going to help your rankings.
Need help with link research?

C3. Link building
Link building should be part of any website’s marketing efforts, as links to the site increase its trust and authority. Without good links, you’ll probably never rank well in search results, even if your site’s content is better than the competitors.
It is an ongoing project, as there will always be new linking opportunities. A page that continually receives new, relevant links is usually considered more trustworthy.
Follow vs. NoFollow – What’s the difference?
Everyone should know these meta tags for links, which dictate whether search engines should follow the link or not. A normal and natural link profile typically has a mix of follow and nofollow links.
“Follow” links (or DoFollow) are followed by search engines and can have a direct impact on the page’s ranking in the search results. They pass “link juice”.
“NoFollow” links are not followed by search engines, but can be used for branding and can drive traffic from ordinary users. While they don’t pass “link juice”, they may still pass trust and authority.
There is debate as to whether a NoFollow link can actually help the ranking and the answer is probably yes, although it is difficult to say how much. Google even takes brand mentions without links into consideration, so a NoFollow link from a trusted site is likely to have a positive impact.
As of September 2019, Google also added the attributes rel=”sponsored” for sponsored content and rel=”usg” for user generated content (such as comments or forum posts). This is to (optionally) further distinguish the types of nofollow links you have. Google will start to take these meta tags as “hints” for which links should pass pagerank.
Example
Follow link: SEOSEON.fi
NoFollow link: SEOSEON.fi
Link types
There are different types of links, including text links, embedded iFrames, form links and image links. Any type of link can improve your site’s visibility and trust. A natural link profile tends to have a mixture of different types of links.
Tip: An image’s title and alt text are used as anchor text for an image link.
Buying links
You may have heard that there is no good way to buy links – That’s not entirely true. Although Google recommends not buying links, the best links are often obtained through partnerships and paid positions.
Never buy link packages! Buying large packs of links is very risky, as it in the worst case scenario can cause Google to completely remove your site from its index – and thus from the search results.
Examples of purchased links
Here are some examples of typical links that can be paid for, but which can still have a positive impact on your visibility in search engines.
Publish in news websites and blogs
Many news sites and blogs offer the opportunity to publish guest articles or so-called “native ads” (ad content that blends in with the rest of the content).
The art of this type of marketing is to write articles that actually add value to the reader and links to your website in a natural way. Therefore, it is not necessary to squeeze in too many keywords and links with exact matches as anchor text. Make sure the article and link are published permanently (so they are not removed in a year or so).
Google’s official guidelines for native advertising are that the content should be marked as advertising material and that the links should have “NoFollow” attributes, but very few companies actually follow these guidelines (as it pays to NOT do so).
The price for an article link is usually between €50 and €2,500, depending on the website.
Links from sports associations
Sports clubs, teams and associations usually link to their sponsors from their website, often directly from the home page (the strongest page). In addition, the associations usually get strong links from e.g. their hometown’s official website, other sports pages and local media, which means their website has a relatively high level of trust.
If it’s just a picture of the sponsor’s logo, you should make sure that the alt tag is filled in with your company name and maybe a brief description (eg: “Company name – Shoe store in Farsta”).
Links from sports associations usually cost between €50 and €3,000 per year.
Banner Links
Banners appear on lots of websites. They can make for good links if the page content is relevant to yours, and the site is trusted enough. A banner link is the same as a banner ad, but appears as a regular image with a regular link, instead of a dynamic ad with an ad link. In short, it means that it is not blocked by adblockers and that the link is considered a regular link to your site.
Google’s guidelines say that all paid links and ads should have the NoFollow attribute. In addition, images with links to other sites are more likely to be ads if they appear in the sidebar or page footer. Thus, it’s generally better to get a banner link in the regular content of the page. The less it looks like an ad, the better.
The cost of a banner is usually between €50 and €10,000, depending on the site, location, duration and size.
Business and link directories
Business directories and other link lists are part of almost every website’s link profile, but it’s not recommended to have too many. A few well-organized and categorized directories can be used to strengthen your link profile. A good directory is one that actually sends traffic to your site. Many directories are free, while others cost up to about €300 per year.
Here are some tips for building directory links:
- Always write a unique description of your business/website
- Supply additional information (contact info, opening hours, etc.) whereever possible
- Stick to the best, most trusted and well-organized directories
- Niche- or industry-specific directories are better than general directories
- Local directories are great for local rankings
Free links
Without a lot of time and good relationships with other website owners, it is really difficult to get good links from reliable websites. However, there are ways to get links for free, which may or may not fit your website.
Content Marketing
Good content sometimes gets 100% natural links from other publishers, who link to the content by their own accord. The best way to get more of those is to create the best, most entertaining and informative content you can. Obviously, to share it, people need to see it first, so here’s some tips to get more eyeballs on it:
- Encourage sharing the content on the page itself
- Share your content in your own social media
- Publish to relevant content aggregators
- Answer relevant discussions in forums and social media with your link
If you write content that provides value, answers people’s questions and is of general interest, it should spread like butter on fresh toast.
Guest Post
Many sites want more content and offers the opportunity to write guest posts. The post can then include a link to your own website. It can also help you reach a new audience.
Unions and associations
Many entrepreneurs and companies are already affiliated with various unions or associations. It is always worth asking if these organizations can link to your business.
Municipalities and cities
Many cities and municipalities list local businesses on their official websites. Are you on the list? If not, it’s definitely worth adding your business, with a link to your website.
These types of links are especially good for local search engine optimization, which means they help you appear in local searches (for people close to your business).
Schools and educational sites
Is your content of sufficient quality and practically useful as source material or learning material? In that case, you may be listed among their sources, or among the school’s tips for further education in a particular subject.
Forum Marketing
Forum links have a bad reputation as being spammy, but that’s not true unless you make it so. If the links come from relevant forum threads, where they actually fit in and contribute to the discussion, then they are good links.
In addition, you can get relevant traffic from these links and perhaps answer customer questions before they even know your site. Just be aware that most forums have suffered from spam and shameless self-promotion in the past, so be respectful and modest.
Blog Portals
There are many blog portals, community sites and other websites that allow you to create your own blog for free. Some of them are centered around a certain topic, such as babies, cars, electronics or fashion. Some of them also allow business blogs.
By writing high quality content to these reliable websites, you can reach people who are interested in your services, but don’t already know who you are. Since these sites already tend to be very trusted, your posts can be ranked highly in the search results immediately.
Other contacts
Do you know someone who has a website? A friend, relative, co-worker, employee or acquaintance? It is free to ask if you can get a link, or publish an article on their website.
“Every marketing campaign should include search engine optimization.”
Need help with link building?

C4. Anchor Text
Anchor text is the word or words used in a link. The anchor text is used to describe where the link leads and thus what the landing page is about. This is why anchor texts are an important part of search engine optimization. There are a couple of different types of anchor texts that can be used, so here is a quick review.
Brand anchor text only consists of the name of the website, brand or company.
Example: The digital marketing agency SEOSEON provides SEO services in all the Nordic languages.
Generic anchor text
A generic anchor text is usually a general call to action, such as “Read more”, “go” or “click here”.
Example: You can find our marketing blog here
Nude URL
The actual web address of the page, that is, its URL.
Example: https://seoseon.com/seo-guide/
Alt text (image link)
When an image links to a page, the anchor text can be entered in the image’s alt tag. It can also be left blank, resulting in a link without anchor text.
Brand + keywords
This type of anchor text consists of both the brand / company and one or more keywords.
Example: Stay up-to-date by reading SEOSEON news every day.
Longtail
Most keywords have so-called “longtails”, which are close and longer variants of the keyword, which usually have lower search volumes. For example: “Blue suede shoes” is a longtail for the keyword “shoes”.
Example: Boost your webshop using seo for e-commerce
Partial Matching
An anchor text with partial matching contains both the keyword and a few other words. It may be the same as longtails, but does not contain keywords alone.
Example: How do I make Google Ads?
Exact match
An anchor text with exact matching contains only the landing page’s main keywords.
Example: Read all about SEO in our guide
Nearby
This simply means that the link is surrounded by very relevant text, even if the anchor text itself does not contain keywords.
Example: Digital marketing should always utilize insights from analytics, as web analytics clearly shows what actually pays off. Learn more about web analytics and improve your site’s revenue.
Recommended distribution of anchor texts
There is no exact science, and it is not something you should focus on, but it is good to have a natural blend of anchor texts. Here is an example of how the anchor texts can be distributed:
Branded anchor text: approx. 70%
Naked URL: approx. 20%
Generic anchor text: approx. 5%
Indirect matching: approx. 1-5%
Direct matching: approx. 1%
D. TECHNICAL SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION
D1. Page Load Speed
Page load speed, or how fast your website loads, is one of the basics of how Google ranks pages in search results, but that’s not the only benefit of having a fast site.
In particular, the mobile users “Bounce Rate”, meaning how many people leave the page immediately, will decrease as the page loads faster.
A web page should always be loaded in less than three seconds. Google also recommends a server response time of less than 200 ms.
Load times also have a direct impact on the conversion rate. According to Neil Patel’s study, a one-second increase in load time can lower the conversion rate by up to 7%. An online store that sells goods for €10,000 a day can lose €2.5 million a year due to an extra second’s delay.
How can I improve website speed?
The page load time depends on several factors, some of which are easier to affect than others. It is the size of the content, especially images or video clips, plus the amount of code, the number of requests made, unnecessary redirects, and the server’s location and speed that have the greatest impact.
You can calculate the load time for your site using Pingdom’s speed test, which also shows graphs of which elements take the longest time to load. Sometimes it can be a certain script or add-on that sabotages everything.
The most important steps to improve page load speed:
Optimize Images – Make file sizes as small as possible, pre-scale images and specify the size in HTML, and use a CDN if possible
Minify the code – CSS, JS and HTML can be compressed
Eliminate unnecessary redirects – Make sure all links are correct (and direct)
Utilize caching – Static content can be stored by the user
Choose a fast, local server – the server location should be as close to the target audience as possible (or use a CDN)
Remove unnecessary content – the smaller, the faster
Need help speeding up your website?

D2. Mobile friendly
Mobile-friendly pages rank better in Google. It is increasingly important absolutely vital to make websites mobile-friendly.
The majority of the browsing now is done via mobile, and Google made its mobile index the main index. This means that your page must be mobile-friendly in order to rank high in the search results.
There are three main ways to make a page mobile-friendly: responsive design, dynamic serving, and separate URLs. Responsive design means that the page is automatically adapted to the specifications of the unit – and is definitely the recommended method.
There is no universal solution, but it is possible to use web analytics to find out if the mobile visitors are doing what is intended.
Summary:
- Create a responsive, mobile-friendly website
- Do not use popups
- Make sure buttons and other elements are far enough apart

D3. Navigation and menus
Site structure and navigation affects search engine optimization, as well as conversion rates.
It should be easy, logical and smooth for a visitor to get to the right page on your website. Design the site structure with categories and sub-categories, according to the keyword plan.
Make it as easy as possible to find the most important categories and create internal links where appropriate. Google may show additional links to subpages on your site if it is structured properly.
Here’s an example of a simple site structure:
- https://example.com/
- https://example.com/category/
- https://example.com/category/product-page/

D4. URL Addresses
We have already mentioned the importance of URLs in connection with anchor texts, but it goes much further than that. A clear and simple URL structure helps both search engines and users understand your website.
Functional formula for URL structure
Short: Brevity is the soul of wit (and good URLs). A short URL is easier to read, understand, remember and repeat.
Clear: You should be able to understand what a page is about just by looking at the URL address.
Organized: With a good site structure, pages and sub-pages are categorized properly – and reflected in the URL.
Example: example.com/category/sub-category/product-page/
In short: Place your most important pages as close to the homepage as possible and add the other pages below them. Ensure you can guess the content of a page by its URL.

D5. Redirects and HTML tags
The importance of redirects
A redirect means that a URL points to another web page and automatically sends the visitor there. This is necessary if an old page has been removed and replaced with a new one, for example if two product categories have been merged into one.
If no redirect is made after a page has been deleted, a user who reaches the page is only met by a “404 error”. If the site has too many broken links, it can have a negative impact on usability – and its visibility in search engines.
Incorrect redirect is one of the most common reasons for a page’s “sudden” collapse in search results.
Correct redirects can fix a broken link, or even help boost certain pages by passing “link juice” from old, expired pages,
A common reason for changing all the URLs of a website is to add an HTTPS certificate, that is, the protocol for the URLs is changed from “http://” to “https://”. Incorrect or missing redirects from http to https can cause lots of errors and warnings to appear.
The most common HTTP response codes:
- 2xx – Successful
- 3xx – Redirect
- 4xx – Client error
- 5xx – Server error
Canonical tag
Rel=”canonical” is an HTML tag created by Google as a solution to the problem of duplicate content. A link can be added to a page that contains duplicate or similar content, to the original page, with a canonical tag, to show Google which page is the original – and should be ranked in the search results.
Note that you should avoid publishing duplicate content whenever possible. A canonical tag should only be used when needed, for example if a product category is paginated with multiple pages of products, but doesn’t differ in content. A canonical tag can then be used to indicate which of the pages is the original one.
If your site only has pages with unique content, which are targeted to different keywords, then you will not need the canonical tag.
Many modern web tools automatically add a link to each page with a canonical tag, although it is not needed. If you need to add it manually, this is done in the HEAD section of the HTML for each page.
sample
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://seoseon.com/seo-guide/” />

D6. Negative SEO
Negative SEO refers to deliberately performing bad search engine optimization, aimed at a competitor. This could mean, for example, building bad, irrelevant links from low-quality websites that point to the competitor’s website. It may also mean republishing competitors’ content, or publishing a large number of negative reviews of the competitor and its products.
Google is doing its best to make this type of attack meaningless. For example, bad links are usually discounted instead of having a negative impact, and links that are suspicious can be dismissed manually.
However, it is important to keep track of the links that come in and how the company is mentioned in external media. Make sure you disavow any links that are clearly irrelevant or spammy and reply to disgruntled customers if possible.

D7. Analysis and SEO tools
In order to continue to improve your results and optimize your website beyond the most basic levels of SEO, you also need to measure and analyze the results. The more attention and effort you put in to analysis, the more insight you can glean. The more insight you have, the more you can improve your site and its rankings.
Best SEO tools
There’s countless SEO tools available online, so we’ll keep it brief. The most important tools for all website owners are Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
In addition, we highly recommend Ahrefs for analyzing links and tracking the rankings for keywords.
Other good tools include:
- Serpbook for keyword tracking
- Keywordtool.io, Semrush and KWFinder for keyword research
- SEOquake (Chrome Extension) for content analysis and identification of NoFollow links

Thank you!
Thank you for reading this guide to SEO. We hope this information will help you on your way to better business!
If you feel that this was a bit too much, or you don’t have enough time for optimization, see our search engine optimization services and let’s climb to the top of Google together!
Anything left unanswered? Disagree with something? Let us know and we’ll update the guide as needed!
SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION
A. INFORMATION
B. INTERNAL SEO
C. EXTERNAL SEO
D. TECHNICAL SEO



